Search Results for: reducing sugar
Reducing sugar
Reducing Sugar Definition What is reducing sugar? The type of sugar that acts as the reducing agent and can effectively... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide Definition In biology and biochemistry, a monosaccharide is a simple sugar that constitutes the building... Read More
Redox reaction
Redox Reaction Definition What are redox reactions? This is a common term in chemistry and biology. In chemistry, a redox... Read More
Isomaltulose
Definition noun plural: isomaltuloses A disaccharide comprised of a glucose monomer and a fructose monomer joined by... Read More
Deoxyadenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxyadenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of adenine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
Deoxyguanosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxyguanosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of guanine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
Deoxycytidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: deoxycytidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of cytosine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Somogyi method
Definition noun The quantitative determination of reducing sugars in terms of Somogyi unit Supplement The Somogyi method is... Read More
Isomaltose
Definition noun plural: isomaltoses i·so·mal·tose, aɪsoʊˈmɔːltəʊz A disaccharide formed from the combination of... Read More
Cellobiose
Definition noun plural: cellobioses cel·lo·bi·ose, ˌsɛləʊˈbaɪəʊz A disaccharide made up of two glucose... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Pyruvic acid
What is Pyruvic Acid? Pyruvic acid is an organic acid that occurs as an intermediate in many metabolic processes. It occurs... Read More
Fructooligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: fructooligosaccharides fruc·to·ol·i·go·sac·cha·ride, ɪhɡəʊˈsækəɹaɪd An... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Hypertonic solution
Hypertonic Solution Definition Hypertonic solution is a relative term that describes the solution having a higher amount of... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Light-independent reaction
The process of photosynthesis is a biological procedure in which plants produce oxygen and energy (sugar) by using light... Read More
Human milk oligosaccharide
Definition noun plural: human milk oligosaccharides An oligosaccharide that occurs in high concentrations and exclusively... Read More
Diaphoresis
What is Diaphoresis? Diaphoresis is referred to excessive or profuse perspiration or sweating which may be due to... Read More
Beta-amylase
'Definition noun, plural: beta-amylases A form of amylase found in bacteria, molds, yeasts, and the seeds of plants that... Read More
Hypertonic
Hypertonic Definition Hypertonic is a term used to describe an entity being in the state of hypertonicity, where there is a... Read More
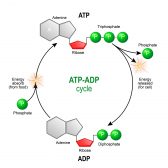
ATP & ADP – Biological Energy
ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate, and is the energy used by an organism in its daily operations. It consists of an... Read More
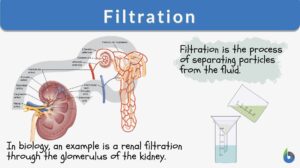
Filtration
Filtration Definition What is filtration? Filtration is separating a solid from a fluid through a porous material that... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More